Hallux Abducto Valgus Bunion Deformity
Overview
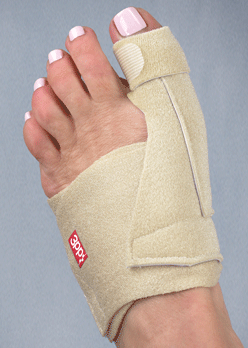 A bunion (hallux valgus) is a deformity of the base joint of the big toe. The cause is not clear in many cases. The deformity may cause the foot to rub on shoes, which may cause inflammation and pain. Good footwear is often all that is needed to ease symptoms. An operation to correct the deformity is an option if good footwear does not ease symptoms.
A bunion (hallux valgus) is a deformity of the base joint of the big toe. The cause is not clear in many cases. The deformity may cause the foot to rub on shoes, which may cause inflammation and pain. Good footwear is often all that is needed to ease symptoms. An operation to correct the deformity is an option if good footwear does not ease symptoms.
Causes
Shoes. The primary cause of bunions is the long term use of shoes, particularly tight-fitting shoes with pointed toes, or high heeled shoes. A study that examined people in cultures that do not wear shoes found no cases of bunions. Genetic. People who have misaligned toes or feet, are flatfooted with feet that roll inwards (over pronation), excessive flexibility of ligaments, abnormal bone structure, or have mechanical instability in the big toe joint are more susceptible to bunions. This is especially common when bunions occur in children or young adults. Injuries or other trauma (sprains, fractures or nerve injuries), neuromuscular disorders (polio or Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease), or limb-length discrepancies (one leg longer than the other). Repetitive stresses to the foot. Bunions are common in ballet dancers and in a few sports. Arthritis.
Symptoms
With Bunions, a person will have inflammation, swelling, and soreness on the side surface of the big toe. Corns most commonly are tender cone-shaped patches of dry skin on the top or side of the toes. Calluses will appear on high-pressure points of the foot as thick hardened patches of skin.
Diagnosis
Looking at the problem area on the foot is the best way to discover a bunion. If it has the shape characteristic of a bunion, this is the first hint of a problem. The doctor may also look at the shape of your leg, ankle, and foot while you are standing, and check the range of motion of your toe and joints by asking you to move your toes in different directions A closer examination with weight-bearing X-rays helps your doctor examine the actual bone structure at the joint and see how severe the problem is. A doctor may ask about the types of shoes you wear, sports or activities (e.g., ballet) you participate in, and whether or not you have had a recent injury. This information will help determine your treatment.
Non Surgical Treatment
The first step in the treatment of Bunions, Corns, and Calluses is determining what is causing the problem. Check with your family doctor or Podiatrist (foot doctor) to find the best solution for your ailment. You can reduce the risk of Bunions, Corns, and Calluses by following these simple instructions. Wear properly-fitting footwear, socks, and stockings (not too tight or too loose). Wear footwear with a wide toe box (toe area). Wear footwear or arch supports which provide proper support, weight distribution, and shock absorption. Maintain a healthy weight. For early-stage Bunions, soaking your feet in warm water can provide temporary relief. 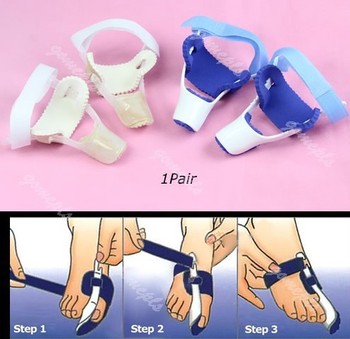
Surgical Treatment
The main goal of surgery is to realign the big toe joint in order to relieve symptoms, correct deformity and restore function. Surgery to remove a bunion is known as a bunionectomy. There are many variations of this operation and the type of surgery performed will vary depending on factors such as the degree of deformity, the strength of the bones, the person's age and the surgeon?s preferred approach. Most surgery involves the removal of the bony outgrowth (exostosis) and the realignment of the bones of the joint. Soft tissue structures such as the ligaments and tendons may be repositioned and the bursa may be removed. The insertion of screws and pins may be required to stabilise the bones in their new, realigned position.
Prevention
Bunions often become painful if they are allowed to progress. But not all bunions progress. Many bunion problems can be managed without surgery. In general, bunions that are not painful do not need surgical correction. For this reason, orthopaedic surgeons do not recommend "preventive" surgery for bunions that do not hurt; with proper preventive care, they may never become a problem.